What Is The Difference Between Silicone Rubber And EPDM?
When selecting a rubber for use, many Engineers end up needing to make a choice between selecting silicone or EPDM. We obviously have a preference for silicone(!) but how do the two match up against each other? What is EPDM and if you find yourself needing to choose between the two, how do you decide? Here is our quick-fire guide to EPDM…
What is EPDM?
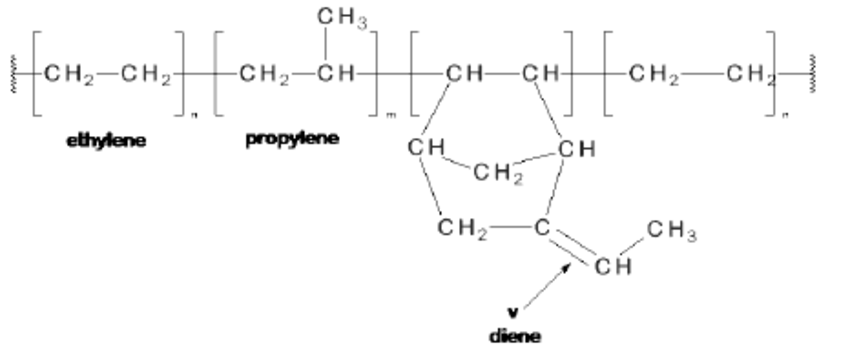
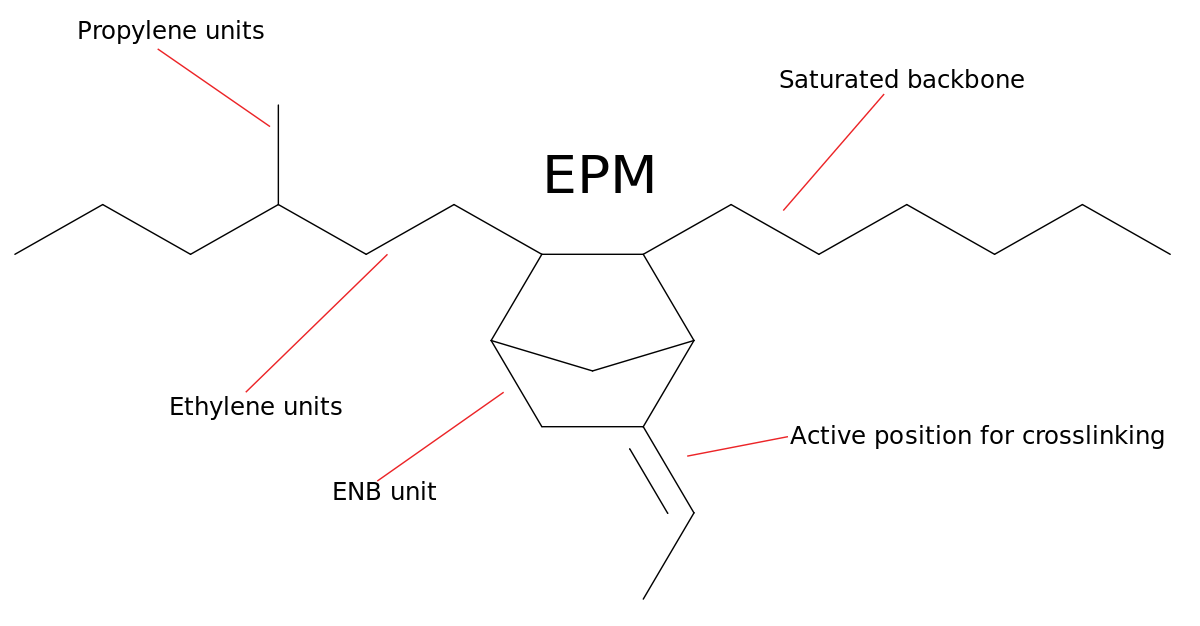
EPDM stands for Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomers and it’s a type of high density synthetic rubber. It’s not as heat resistant as silicone but is able to withstand high temperatures up to 130°C. Because of that it’s used as a component within a wide variety of industries including industrial, construction and automotive. In lower temperatures, EPDM will reach brittle point at -40°C.
EPDM is also popular as an outdoor rubber as it’s resistant to weathering including acid and alkali resistance. As such, you’ll typically find it being used for things such as window and door seals or waterproofing sheets.
EPDM also has good abrasion, cut growth and tear resistance.
What more can silicone offer?
While silicone and EPDM share a number of features such as excellent environmental resistance, there are also a number of significant differences and it’s important to acknowledge these when making your purchasing decisions.
Silicone is a mix of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and silicone and this mixture gives a number of benefits which EPDM doesn’t. Silicone is much more heat resistant, being able to withstand temperatures up to 230°C while maintaining its physical properties. What’s more, it’s also a sterile elastomer and as such is popular within the food and beverage industries. In lower temperatures silicone also exceeds EPDM and will not reach brittle point until -60°C.
Silicone is also stretchier and provides more elongation than EPDM. It can also be formulated to be just as tear resistant as EPDM. Both of these aspects make it ideal for use as vacuum membranes in machines used to produce solar panels and laminated furniture, often called vacuum forming machines.
Silicone is a more stable elastomer and as a result buyers feel that silicone is better as a more secure long-term solution because of this. Although silicone is seen as the more costly out of the two, EPDM’s lifespan is often shorter than that of silicone and therefore has to be replaced in application more often. This results in the long term cost exceeding that of silicone.
Finally, while both EPDM and silicone will swell if placed in oil for long periods of time at high temperatures, silicone has resistance to food oils at room temperature which is why it is used in food oil processing as seals and gaskets for processing machinery.
How to choose between the two?
While this short guide simply summarises some of the differences between the two the best way to determine which rubber you need is to understand the purpose of use and exact application. Identifying how you will want to use it, what conditions it will be subject to and how you need it to perform will allow you to have a much clearer view as to which rubber to choose.
Also, be sure to consider aspects such as the strength, flexibility and weight the material will need to withstand as these can also be crucial deciding factors. When you have this information our comprehensive guide to Silicone Rubber vs EPDM can provide you with the in-depth information you need to make your final determination.
If you would prefer to discuss your project requirements with one of our team then someone is always available. Just contact us.
Post time: Feb-15-2020